Multi-tier Application Deployment
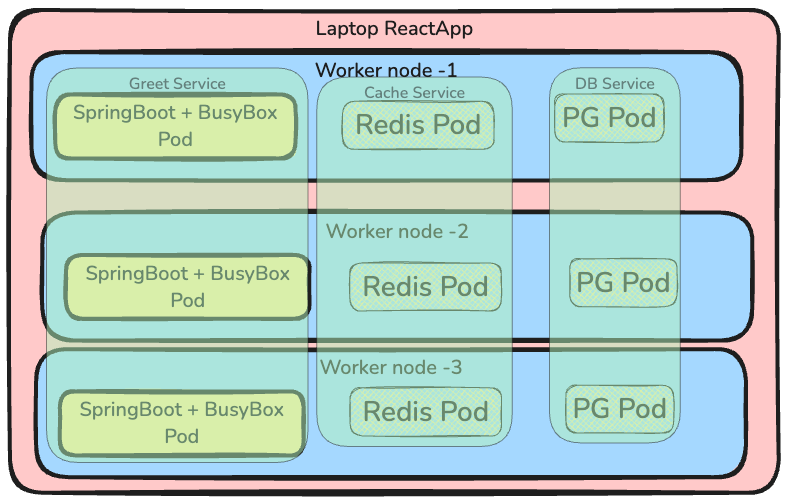
Let's explore deploying a multi-tier application in Kubernetes. Our setup includes:
- 1 Control-plane node
- 3 Worker nodes
-
A Greet user app with:
- Front-end: ReactJS
- Back-end: Spring-Boot with a single REST endpoint /greet
- Redis: For storing/reading recently greeted users
- H2 DB: For storing recently greeted users (fallback for Redis)
Deployment Steps
-
Create a secret for your Docker registry:
sudo kubectl create secret docker-registry my-registry-secret \ --docker-username=username \ --docker-password=password \ --docker-email=my@mail.com -
Deploy Redis:
kubectl apply -f deploy-redis.yaml kubectl apply -f service-redis.yaml -
Deploy Spring Boot app:
kubectl apply -f deploy-greetapp.yaml kubectl apply -f service-redis.yaml -
View your deployments, services, and pods:
kubectl get deployments kubectl get services kubectl get pods
Deployment
- Create ReactJS app on the control plane host
- Create OpenJDK base image for SpringBoot container. (Using OpenJDK base image to create a large size image.
- Push to DockerHub
- Use readymade Redis image from Docker Hub
- Create deployment and service manifests (1 replica for Redis, 3 for Spring Boot)
- Deploy Redis and Spring Boot app
Node Failure Simulation
Shutdown one node and observe pod rescheduling. Then shutdown another node to see the impact. kube-scheduler automatically creates pods on other available nodes.
Memory Pressure
Symptom
kubectl get pods would never have pods in
"Running" state. (verify using
kubectl get pods)
Simulation
If all pods are running then simulate memory pressure using deployment scale.
kubectl scale deployment greetapp --replicas=<INT>Debugging
-
kubectl describe node <node-name>|grep -i pressureMemoryPressure False KubeletHasSufficientMemory kubelet has sufficient memory available MemoryPressure Unknown NodeStatusUnknown Kubelet stopped posting node status.
-
kubectl get podscommand will show multiple entries with evicted pod. -
sudo journalctl -u kubelet -fwill show eviction logs
Solution
- Increase memory of the VM or reduce pod count.
- Stop unused containers/pods.
- Change eviction thresholds.
Disk Pressure
Symptoms
kubectl get pods would never have pods in "Running" state. (verify using kubectl get pods)
Simulation
If all pods are running then simulate disk pressure by deleting and creating deployments multiple times of multiple version of same app.
Multiple pull different version, fills the disk space.
Debugging
-
kubectl describe node <node-name>|grep -i pressureDiskPressure False KubeletHasNoDiskPressure kubelet has no disk pressure DiskPressure Unknown NodeStatusUnknown Kubelet stopped posting node status.
kubectl get podscommand will show multiple entries with evicted pod.sudo journalctl -u kubelet -fwill show eviction logs
Solution
- Increase disk space of the VM.
- Remove unused images:
sudo crictl rmi --prune - Remove stopped containers:
sudo crictl rm $(sudo crictl ps -a -q --state=exited) - Change eviction thresholds.
IP Addresses in Kubernetes
Before actual deployment, imagine if an app is already deployed. This is where K8s starts getting complicated and leaves systems like Minikube way behind.
Now ask yourself, how would you access the app in kubernetes?
curl <which-ip?>:30008/api/greet -X POST -H "Content-Type: application/json" -d '{"name":"value2"}'Careful, let's dissect this.
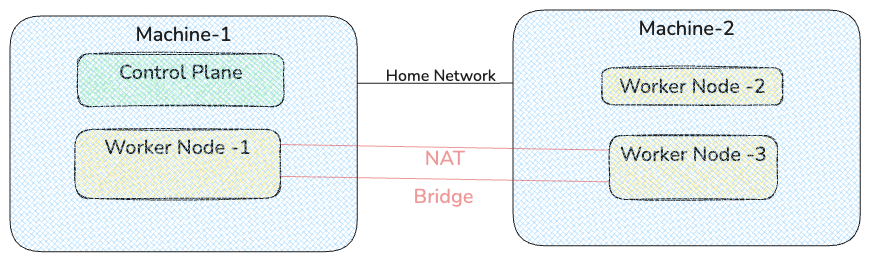
Types of IP Addresses in K8s
1. Cluster IP Range
This is the overall CIDR range for the entire cluster's pod network.
--cluster-cidr=10.85.0.0/16 parameter in kubeadm is used to control this.
2. Pod IP
- This refers to a subnet of the cluster-cidr assigned to a specific node.
- The pod IP is an ephemeral address, meaning it changes when the pod is recreated or restarted.
- A Pod's IP address is assigned by the Container Network Interface (CNI) plugin.
- By Default K8s uses bridge CNI. It does not allow pod to pod communication on different nodes. But it allows pod to pod communication on same node.
Learn more: How a Kubernetes Pod Gets an IP Address
3. Node IP
- Each node in a Kubernetes cluster has a unique IP address, known as the node IP.
- This IP address is used for communication between the node and other nodes in the cluster, as well as for external communication.
- The node IP is a stable address that remains unchanged unless the node is replaced or reconfigured.
- Assigned by OS (DHCP or manual)
4. Service IP
- A Service IP, also known as a Cluster IP, is a virtual IP address that is assigned to a Service object.
- A Service is an abstraction that defines a logical set of pods and a network policy for accessing them.
- The Service IP is used for external access to the Service, and it is load-balanced across the pods that are backing the Service.
- Service IPs are stable unless the Service is updated or deleted.
--service-cluster-ip-range=10.96.0.0/12parameter in kubeadm is used to control this.
Additional Notes
- If you omit the
--apiserver-advertise-addressflag, kubeadm will use the IP address of the default network interface (usually the primary network interface) as the advertised IP address. - If VM has two or more NICs, in Ubuntu these interfaces have priority decided by route metric (lower value means higher priority).
- So the IP of NIC which has the higher priority is advertised by kubeadm.